Policy Advocacy Activities
As a non-profit, non-governmental organisation, Free Software
Foundation Europe works to create general understanding and
support for Free Software and Open Standards. The following
activities are concrete actions that we take in the areas of
public awareness, policy advocacy, and legal support.
Since its foundation in 2001, the FSFE has been working every
single day to further Free Software in Europe and beyond. With
our concrete activities, based upon the three pillars of our work, we
focus on protecting and extending user rights. Some of our
actions run for many years, some are aimed at short-term
developments, but all are part of our mission: empower users
to control technology.
Another major part of our work consists of continuous engagement
and background work. We are present at dozens of conferences per year,
support and maintain an excellent community, and
provide it with helpful resources. Furthermore, we are a
prominent contact point for all questions and enquiries around
software freedom, Open Standards, and user rights. We also provide basic education resources on Free Software legal and licensing issues.
We need political change to strengthen Free Software. Learn more about how we
achieve this.
-
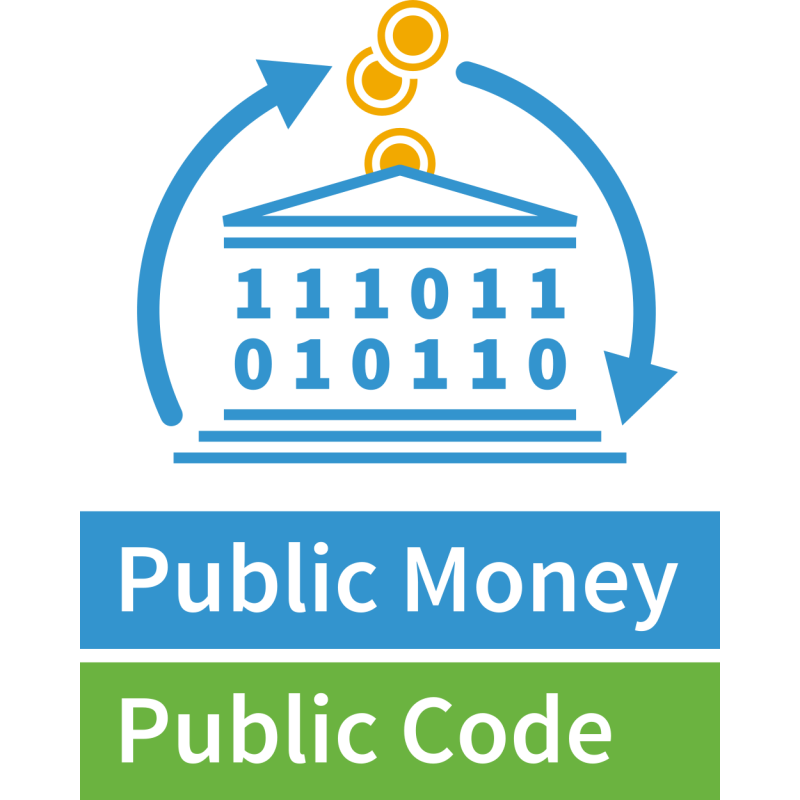
Why is software created using taxpayers' money not released as Free Software? We want legislation requiring that publicly financed software developed for the public sector be made publicly available under a Free and Open Source Software licence. If it is public money, it should be public code as well. Code paid by the people should be available to the people!
-

Although digital devices are ubiquitous today, the number of devices on which users cannot run Free Software is exponentially increasing. The consequence is an increased loss of control over users’ technology. Device Neutrality aims to enable end-users to bypass gatekeepers to have a non-discriminatory use of Free Software on their devices.
-

Device Neutrality is the policy concept to regulate monopoly over
devices and re-establish end-user control over their digital equipment.
The Digital Markets Act (DMA) regulates the economic activity of large
digital platforms and introduces Device Neutrality in the EU
legislation, fostering access to Free Sofware in Devices.
-

Although we should be free to choose the technical devices we use in our private lives, some European Internet Service Providers are dictating which device their customers have to use to connect to the Internet, or discriminating against owners of alternative devices. This undermines our basic freedom of choice.
More Policy Activities
-

An EU regulation may make it impossible to install a custom piece of
software on most radio devices like WiFi routers, smartphones, and
embedded devices. It requires hardware manufacturers to implement a
barrier that disallows users to install any software which has not been
certified by them.
-
What could be a better time to ask politicians about their stance on Free
Software and Open Standards than the run-up to an election? We believe we
can and should raise these issues in all elections, European, national,
regional and local. Depending on the electoral system and culture, we use
different strategies and tools.
We are working towards a world where software does what software
users want it to do. For this, software users must be able to
participate in the development and distribution of the software.
Software patents block this goal by adding legal and financial
risks to software development and distribution and by giving the
patent holders legal power to completely prohibit software
developers from using the patented ideas.
The PDFreaders initiative aims to shine a spotlight on government
organisations that promote proprietary PDF readers. With the help of
activists across Europe, we have contacted these organisations and told
them how they can improve their websites to respect our freedom. On
pdfreaders.org
we present Free Software PDF readers for all major operating systems.
In 2001 the European Union started investigating Microsoft's dominant
position in the market for desktop operating systems. The FSFE represented
the interests of Free Software developer as a public interest organisation
who cannot be bought off. Thanks to the excellent work by all involved
parties, the case was won in all rulings up to the European Court of
Justice in 2012.
This activity was specifically targeted at the Dutch education sector, with
the aim of enabling citizens to have free access to education and public
institutions, both online and offline. By promoting the mandatory use of
Open Standards and platform-independent access to all materials, students
and parents will be able fulfil their potential for personal growth and
development without being dependent on a company.
The European Commission funds research and development through official
framework programmes (FP for short). From 2007 these framework programmes
were used to select projects for support until 2013. The FSFE played a
central role in supported projects related to Free Software.
Le Forum de la Gouvernance Internet (IGF) est un forum de discussion des politiques globales au sein des Nations Unies, établi lors du Sommet Mondial de la Société de l'Information (WSIS) des Nations Unies. La FSFE suit les travauxde l'IGF pour s'assurer que les discussions politiques en cours ne mettent pas en danger les libertés numériques en général et le Logiciel Libre en particulier.
Since the beginning of the standardisation process for Microsoft's Office
Open XML - OOXML (hereafter MS-OOXML), the FSFE has raised serious doubts
about whether MS-OOXML can be considered open. FSFE was the first to raise
the issue in the community, led the movement against the standardisation
of MS-OOXML, and has been closely following developments over the years.
Une seconde directive portant sur l'application des "droits à la propriété intellectuelle" a été proposée par la Commission Européenne. Elle vise à criminaliser toutes les infractions "intentionnelles" ou à une "échelle commerciale", et à donner le droit aux détenteurs des droits de participer aux enquêtes. La FSFE va démontrer aux institutions européennes comment une telle loi peut encourager les abus du système judiciaire et avoir un effet négatif sur certaines activités pourtant légales.
L'Organisation Mondiale de la Propriété Intellectuelle (OMPI) est l'une des 16 institutions spécialisées du système des Nations Unies. Son rôle est d'administrer les 24 traités internationaux ayant trait aux différents aspects de la propriété intellectuelle. En tant qu'observateur de l'OMPI et en union avec une coalition mondiale d'autres acteurs aux buts similaires, la FSFE travaille à remodeler cette institution en une "Organisation Mondiale de la Richesse Intellectuelle" ("World Intellectual Wealth Organisation.")
Le Sommet Mondial sur la Société de l'Information (SMSI) est une conférence de
l'ONU, organisée par l'ITU (International Telecommunication Union), au cours de
laquelle devraient être posées d'importantes pierres angulaires pour la société
de l'information et de la connaissance. La FSFE participera, avec d'autres
sociétés civiles, pour s'assurer que les principes de l'ère numérique ne soient pas
déterminés seulement par l'industrie des médias et les gouvernements, et que les
droits de l'homme ne seront pas invalidés techniquement.
Funding of research and development by the European Commission is usually
done within the "framework programmes" (FPs). These last for four years and
FP6 started officially on December 17th, 2002. The FSFE sought to help with
Free Software related activities in FP6.
The goal was to have Free Software classified by UNESCO as an Intangible
World Heritage and registered in the World Memory Register (another UNESCO
project). The Free Software community and UNESCO share the same values of
freedom, equality and fraternity. Such recognition would be a great boost
for Free Software.
The European Copyright Directive (EUCD) was the European equivalent of the
US Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA). These laws lead to the
creation of monopolies and cartels, and pose serious obstacles to freedom
of speech and the press by providing means for digital censorship. The
FSFE has been actively involved in opposing such harmful legislation.





